


Most Popular Posts
View All
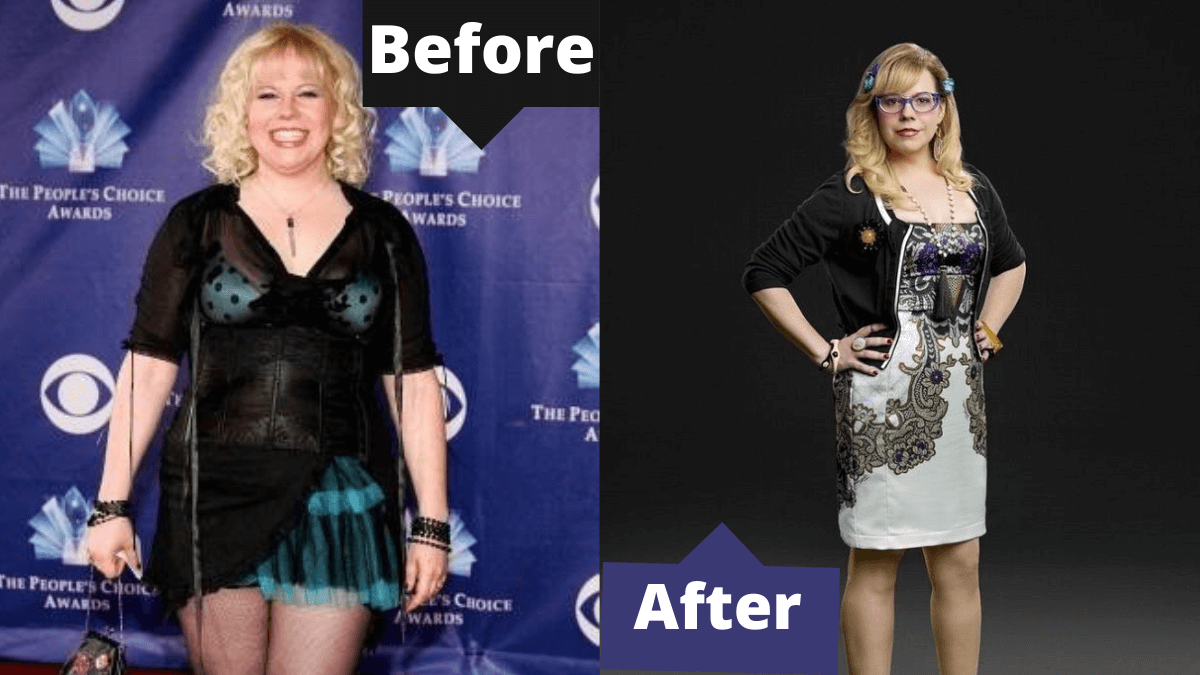
How To Break Up With Someone? Ways For A Smooth Breakup
It might seem a little weird if you find someone searching the internet to know how to break up with someone. However, breakups are nothing alien in today’s society. In …

How to Start Podcasting? Learn The Steps
Nowadays, podcasts have become pretty popular among people of all ages. Often there are many inspirational podcasts that we listen to. So if you are wondering how to start podcasting, …
Latest Posts
View All
Johnny Depp net worth 2023 luxury lifestyle, career & early life
Johnny Depp has been one of the most well-known celebrities in the world, thanks to his long-running feud and contentious divorce from Amber Heard. Aside from his much-discussed personal life, …
Latest Posts
View All
How to activate Peacock TV on Any Devices: All You Need to Know
Over-the-top (OTT) streaming provider Peacock is owned by NBCUniversal, a Comcast subsidiary. The service primarily offers a number of movies, TV shows, and news stories from NBCUniversal Studios and other …

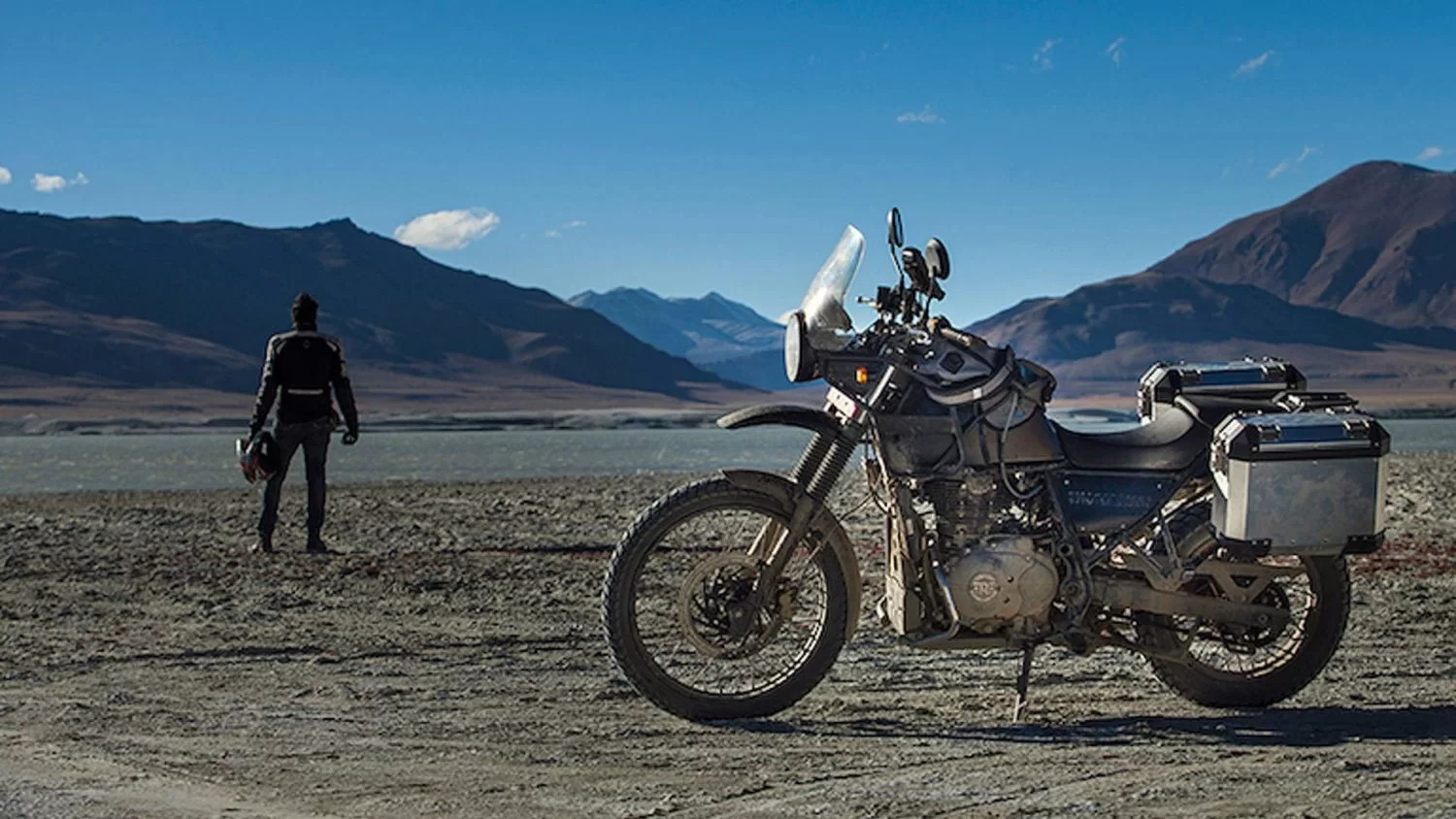
Best Himalayan Treks to do in India
Trekking in India has become one of the most popular adventurous activities. There are many trekking spots in the Himalayas and people from all over the world come for trekking. …
Latest Posts
View All
YSR Rythu Bharosa List 2023: Online Payment Status 1st, 2nd Farmer List
Every day, the Andhra Pradesh government introduces new programmes to enhance the economic situation of their state’s farmers. On the same track, he has recently launched the YSR Rythu Bharosa …























